What is Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency, also known as crypto, has been changing the way that finance operates for several years now. Before diving deeper, let’s cover some crypto basics to help you understand the fundamental concepts and principles of cryptocurrency.

Once deemed a fad by Bitcoin skeptics back in the early 2010s, crypto has now gone mainstream, being featured in the media and with some coins soaring to unfathomable heights, producing thousands of crypto millionaires and billionaires.
But what actually is cryptocurrency? In this article, we’ll run over the history, what blockchain technology is and how exactly you can get involved.
Understanding the Basics of Cryptocurrency: Brief History
The first cryptocurrency (the Bitcoin system) was established in 2008 when the pseudonymous Satoshi Nakamoto invented a decentralized electronic cash system that uses a peer-to-peer distributed timestamp server to prevent double-spending.
This distributed server generates computational proof of the chronological sequence of transactions.
In layman’s terms, it’s a digital payment system that doesn’t rely on banks or other intermediaries to verify transactions; all that’s needed are other computers that can verify transactions on a blockchain digital database. These transactions are recorded on a public ledger for anyone to see.
Every Bitcoin transaction receives a digital timestamp when it is confirmed.
Every bitcoin transaction receives a digital timestamp when it is confirmed.
How Does Cryptocurrency Work?
Cryptocurrency operates on a blockchain network, which is a decentralized and distributed ledger that records all transactions across a network of computers, known as nodes. This ledger is collectively maintained by all participants, ensuring that no single entity has control over the entire network.
Blockchain Network:
- A decentralized and distributed ledger.
- Maintained by nodes (computers) across the network.
- Ensures transparency and security without centralized control.
Each crypto transaction made with cryptocurrency is grouped into a “block” and then added to the “chain” of previous transactions, creating a secure and transparent record. This structure makes it nearly impossible to alter or tamper with past transactions, as doing so would require changing all subsequent blocks.
Transaction Process:
- Transactions are grouped into blocks.
- Blocks are added sequentially to form a chain (blockchain).
- This creates a secure, immutable record of all transactions.
A cryptocurrency transaction involves the exchange of digital currencies and is recorded on the blockchain to ensure security and transparency.
The security of these transactions is ensured through cryptographic techniques. Public and private keys are fundamental components of cryptography, used to authenticate transactions and confirm that funds can only be accessed by their rightful owner.
Cryptographic Security:
- Public and Private Keys: Used to authenticate and secure transactions.
- Ownership Verification: Ensures only the rightful owner can access the funds.
When a transaction is initiated, it is broadcast to the entire network, where miners or validators confirm its legitimacy by solving complex mathematical puzzles. Depending on the blockchain, this process is known as proof-of-work (PoW) or proof-of-stake (PoS). This verification adds a layer of security, making it nearly impossible to alter or counterfeit the transaction. of
Transaction Verification:
- Broadcast to Network: Transaction is sent to all nodes.
- Miners/Validators: Confirm legitimacy by solving mathematical puzzles.
- Proof-of-Work (PoW) or Proof-of-Stake (PoS): Methods used to secure the blockchain and verify transactions.
This decentralized, cryptographically-secure system ensures the integrity and transparency of cryptocurrency transactions, providing a robust foundation for the functioning of digital currencies.
What Are Digital Assets?
Digital assets encompass a wide range of intangible assets that exist in digital form. This includes everything from cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin to digital art, music files, and even domain names. Crypto assets specifically refer to digital currencies and tokens that are secured by cryptographic methods, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum.

Cryptocurrencies are a subset of digital assets, designed as a medium of exchange, utilizing blockchain technology to achieve decentralization, transparency, and immutability.
While digital currency refers specifically to electronic forms of traditional currency issued by governments or financial institutions, digital assets are broader in scope, including cryptocurrencies as well as other blockchain-based tokens that represent ownership or access rights to various forms of digital content or physical assets.
Types of Cryptocurrencies
Bitcoin, the first and most well-known cryptocurrency, remains the cornerstone of the crypto market. Created in 2009 by the pseudonymous figure Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin is built on its own blockchain, known as the Bitcoin blockchain.
Bitcoin is often considered the most valuable cryptocurrency due to its widespread adoption and strong network. This blockchain is significant for being the first implementation of a decentralized ledger, laying the groundwork for all subsequent cryptocurrencies.
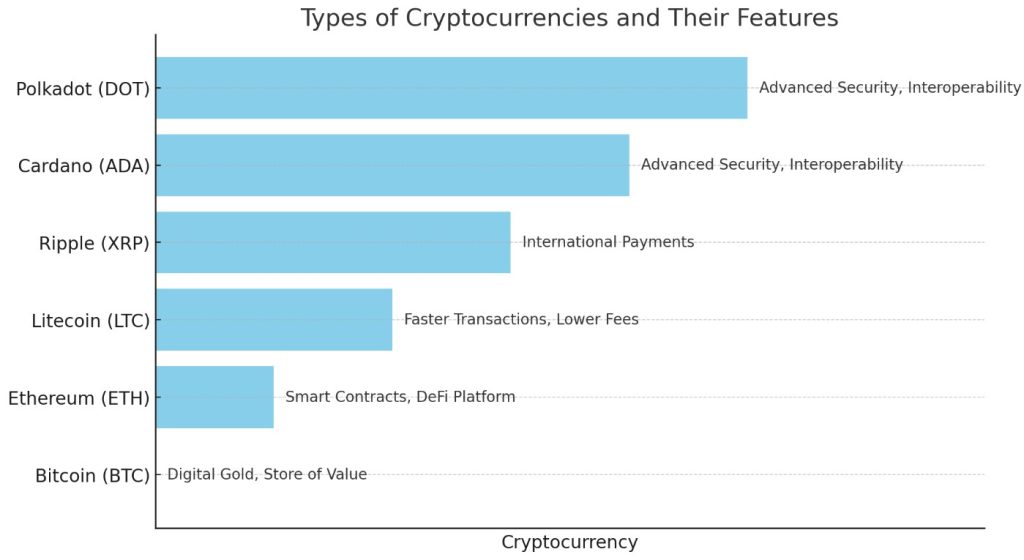
Bitcoin (BTC):
- The original cryptocurrency and digital gold.
- Operates on the Bitcoin blockchain, the first decentralized ledger.
- Primarily used as a store of value and a medium of exchange.
Ethereum, another key player in the crypto world, introduced the concept of smart contracts—self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code. The Ethereum blockchain enables developers to build decentralized applications (dApps) on top of its network, making it a central hub for innovation far beyond simple transactions.
Ethereum (ETH):
- Introduced smart contracts and dApps.
- Built on the Ethereum blockchain, known for its versatility.
- A platform for decentralized finance (DeFi) and other blockchain-based services.
Beyond Bitcoin and Ethereum, a wide range of alternative cryptocurrencies, commonly known as altcoins, have emerged. These include coins like Litecoin, Ripple (XRP), and newer entrants such as Cardano and Polkadot. Each altcoin offers unique features or improvements over Bitcoin, such as faster transaction speeds, lower fees, or enhanced privacy.
Altcoins:
- Litecoin (LTC): Known for faster transaction times and lower fees compared to Bitcoin.
- Ripple (XRP): Focuses on facilitating international payments with minimal transaction costs.
- Cardano (ADA) and Polkadot (DOT): Newer platforms offering advanced blockchain features, including enhanced security and interoperability.
The expanding ecosystem of altcoins and crypto coins reflects the growing possibilities within the cryptocurrency space. Developers and entrepreneurs continue to experiment with blockchain technology, leading to innovative applications that push the boundaries of what these digital assets can achieve.

The Role of Blockchain Technology
What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain technology is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers in a way that ensures the security and transparency of the data. At its core, blockchain is composed of blocks—units that store data, each connected to the previous block, forming a chain.
This architecture ensures that once data is recorded, it cannot be altered without altering all subsequent blocks, which would require consensus from the entire network. This immutability is a key principle of blockchain, along with decentralization, which distributes control across many participants rather than a single authority.
Transparency in the blockchain is achieved through its public nature, where all participants can view the transaction history, ensuring accountability. Security is maintained through cryptographic methods, which protect the integrity of the data and ensure that transactions are legitimate.
How Blockchain Supports Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum operate on blockchain networks, which provide the framework for secure, transparent, and decentralized transactions. Each transaction is recorded on the blockchain, creating an unchangeable and transparent history of exchanges.
Crypto mining is the process by which transactions are verified and added to the blockchain, ensuring the integrity and security of the network.
The decentralized nature of blockchain means that no single entity controls the network, reducing the risk of fraud or tampering.
Cryptographic techniques, such as hashing and digital signatures, play a crucial role in securing these transactions. Hashing converts transaction data into a fixed-size string of characters, ensuring the data’s integrity.
For example, in the Bitcoin network, each block contains a hash of the previous block, linking them together and ensuring that any attempt to alter a transaction would be immediately evident as the hash would no longer match.
Digital signatures allow participants to verify ownership and authenticate transactions, ensuring that only the rightful owner can transfer their cryptocurrency.
For instance, when a Bitcoin transaction is initiated, the sender signs it with their private key, which is then verified by the network using the corresponding public key. This process ensures that the transaction is legitimate and that the funds cannot be spent by anyone other than the owner.
These cryptographic techniques collectively ensure that the blockchain remains secure, even as it processes vast amounts of data across a decentralized network.
This level of security and transparency is what underpins the trust in blockchain-based cryptocurrencies, enabling them to function effectively in a decentralized manner.
Blockchain Applications Beyond Cryptocurrencies
While blockchain technology was initially developed to support cryptocurrencies, its applications have expanded into various industries.
In decentralized finance (DeFi), blockchain enables peer-to-peer financial services like lending, borrowing, and trading without the need for traditional intermediaries like banks.
For instance, platforms like Uniswap use blockchain to facilitate the decentralized trading of digital assets.
Financial institutions are also exploring blockchain for its potential to streamline processes, reduce fraud, and enhance transparency. For example, banks are experimenting with blockchain to improve the efficiency of cross-border payments and to create secure digital identities.
The immutable and transparent nature of blockchain makes it an appealing solution for industries that require secure, traceable, and verifiable records.
The cryptocurrency market is known for its volatility, influenced by various factors such as demand and supply dynamics, regulatory changes, and technological advancements.
Through these diverse applications, blockchain technology is proving to be a transformative tool, extending far beyond its roots in cryptocurrency.
How Blockchain Powers Cryptocurrency Transactions?
In the process of inventing this payment system, Satoshi also pioneered the first blockchain database, which we previously mentioned, to facilitate secure and transparent crypto transactions. Since then, many other cryptocurrencies have emerged, many of which use a similar type of blockchain technology as Bitcoin.
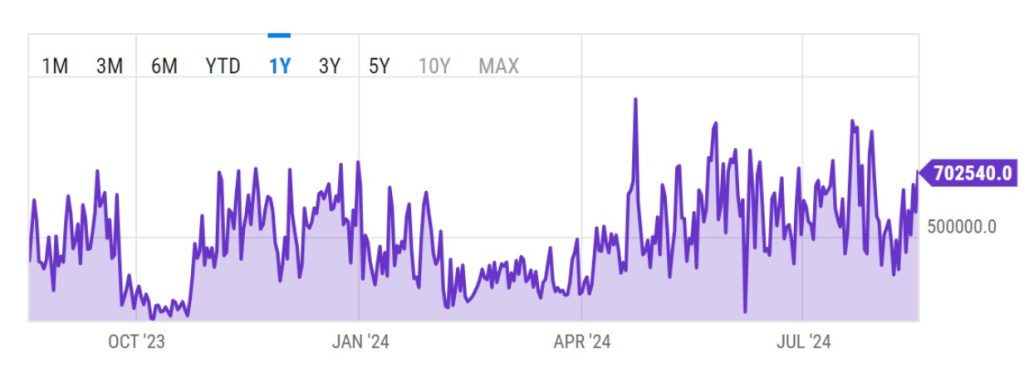
This reliance on a public ledger to record and track transactions remains the common thread between cryptocurrencies. A prominent example is August 2024, when the average number of Bitcoin transactions per day was around 700,000.
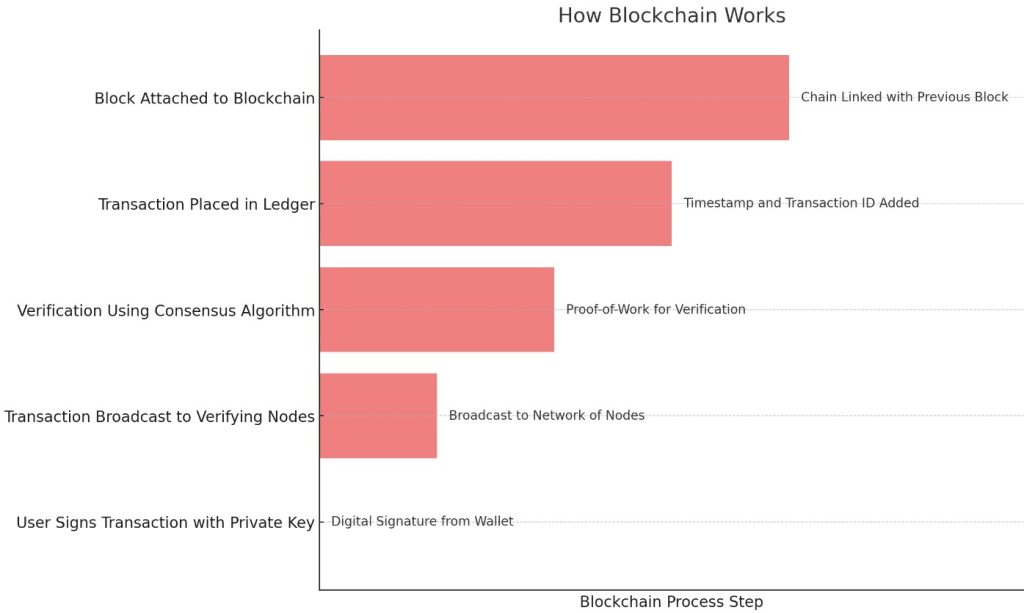
Essentially, the blockchain works like this:
- A user starts a transaction, signing it with their private key to prove it’s from their particular wallet. Think of it like a digital signature.
- The transaction is broadcast to the verifying nodes, which can be anyone with a computer or a set of verified nodes, depending on the cryptocurrency.
- The transaction is verified using a consensus algorithm. Bitcoin, for example, uses proof-of-work, which requires computational power to solve complex mathematical problems and verify the transactions. This ensures every node has a copy of the same ledger.
- Once the nodes verify the transaction, it’s placed in the ledger with a timestamp and transaction ID.
- When the block is completed, it gets attached to the previous block, forming a blockchain.
As the technology has progressed, we’ve seen hundreds of use cases emerge.
From decentralized applications and smart contracts on Ethereum to Golem, which lets people rent out their computing power to form a supercomputer capable of running energy-intensive scientific calculations and CGI rendering, it seems endless what crypto can do.
How Are Transactions Validated?
Because there’s no oversight by central banks or authorities to verify transactions, it must be done on the blockchain. The nodes connected to the network must verify that they have the same copy of the ledger as everyone else.
The Process of Mining Cryptocurrency
What is Cryptocurrency Mining?
Crypto mining is the process by which transactions are verified and added to the blockchain, involving solving complex mathematical puzzles to ensure the integrity and security of the network.
Miners, who perform these tasks, are rewarded with newly minted cryptocurrency tokens. This process is essential to maintaining the decentralized nature of blockchain networks.
Key Points:
- Verification: Miners confirm and validate transactions on the blockchain.
- Rewards: Successful miners receive cryptocurrency tokens as compensation.
- Decentralization: Mining helps maintain the security and decentralized nature of the network.
Example: In the Bitcoin network, miners solve cryptographic puzzles to add new blocks to the blockchain, receiving Bitcoin as a reward. This ensures that all Bitcoin transactions are verified and recorded in the public ledger.

Mining Cryptocurrency: Computing Power and Energy Consumption
Cryptocurrency mining demands immense computing power due to the complexity of the puzzles miners must solve. This computational effort requires substantial energy, leading to significant environmental concerns.
- Energy Consumption: Bitcoin mining, for example, consumes more electricity annually than some entire countries. This has sparked debates about the sustainability of mining operations.
- Specialized Hardware: Miners often use ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits), which are specialized devices designed to optimize mining efficiency and solve cryptographic puzzles faster than general-purpose computers.
Example: A large Bitcoin mining farm in Iceland leverages the country’s geothermal and hydroelectric power to run thousands of ASICs, aiming to minimize its environmental impact while maintaining high mining efficiency.
Consensus Protocols: Proof-of-Work and Proof-of-Stake
There are a few ways that these incentives work, otherwise known as consensus protocols. The most common are proof-of-work (PoW) and proof-of-stake (PoS).
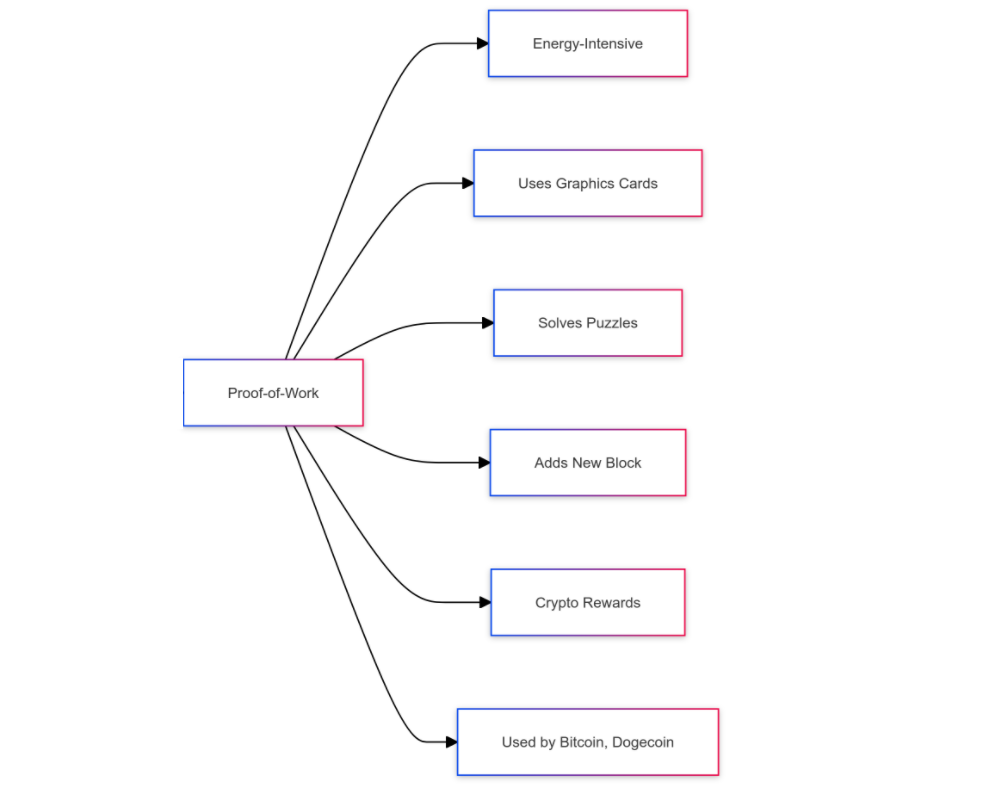
- Proof-of-work: This system uses an energy-intensive process that uses expensive graphics cards to generate the code that solves a computational puzzle. If they solve the puzzle, they are granted the right to add a new block of transactions; in doing so, they receive rewards in the form of the crypto they’re validating.
Any fees associated with the transactions included in the new block are also paid out to the successful miner. This is the system used by Bitcoin, Dogecoin, and the original version of Ethereum.
- Proof-of-stake: Here, computational power isn’t used, and instead, node operators only need to lock away the coin they want to validate, known as staking, showing their commitment to the longevity of the network. Many PoS cryptos require validators to lock away their coins for at least six months.
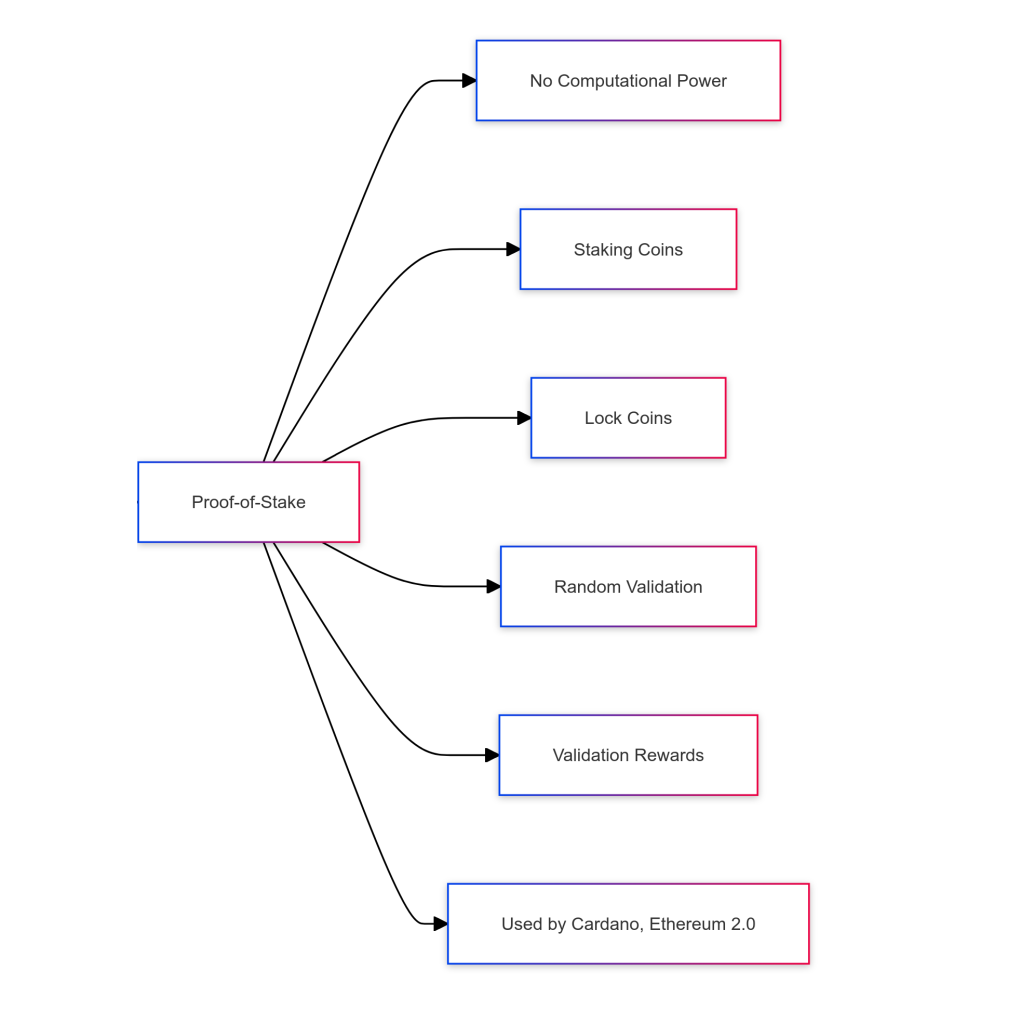
The protocol then randomly assigns validation tasks to pools of nodes, paying out rewards to successful validators. This is the system used by Cardano, Solana, and Polkadot. Ethereum 2.0 also uses PoS.
The Future of Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrency as an Investment
Cryptocurrency investing is often seen as a speculative venture due to the market’s high volatility. Prices can swing dramatically in short periods, offering the potential for significant rewards but also posing considerable risks. For individual investors, the allure of high returns is tempered by the possibility of substantial losses, especially in a market driven by sentiment and speculative behavior.
Key Risks and Rewards:
- Rewards: Early adopters of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum have seen tremendous returns on their investments, sometimes multiplying their initial investments by several hundred or even thousand percent.
- Risks: However, the lack of regulation, market manipulation, and extreme price volatility make cryptocurrencies a risky investment, where investors can lose a significant portion of their capital.
Institutional investors are increasingly entering the cryptocurrency space, drawn by the potential for diversification and high returns. However, they must also navigate these same risks, in addition to concerns about regulatory scrutiny and the security of their investments.
The Impact of Cryptocurrency on Traditional Finance
Cryptocurrencies differ fundamentally from fiat currencies and traditional finance systems. Unlike fiat currencies, which are issued and controlled by central banks, cryptocurrencies are decentralized and operate on blockchain networks.
This decentralization allows for peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries like banks, potentially reducing transaction costs and increasing financial inclusion.

Comparison with Traditional Finance:
- Fiat vs. Crypto: Fiat currencies are backed by governments, whereas cryptocurrencies are backed by cryptographic algorithms and the trust of their users.
- Potential Reshaping of Finance: Cryptocurrencies could challenge traditional financial systems by providing alternatives to centralized banking, enabling cross-border transactions without the need for foreign exchange fees, and offering financial services to unbanked populations.
The rise of decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms exemplifies how blockchain technology can disrupt traditional finance, allowing users to lend, borrow, and trade assets without the need for traditional banks.
The Future of Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies
Looking ahead, blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies are poised for continued innovation and expansion. As the technology matures, we may see greater mainstream adoption, with cryptocurrencies being used more widely for everyday transactions.
Future Developments:
- Mainstream Adoption: The integration of blockchain into various industries and the potential for cryptocurrencies to be used as a standard form of payment could drive broader acceptance.
- Regulation Challenges: However, the path to mainstream adoption will likely face hurdles, including regulatory challenges as governments seek to impose rules on an inherently decentralized system.
The balance between innovation and regulation will be crucial in determining the future trajectory of cryptocurrencies and their role in the global financial system.
About Cryptocurrency Payments – Bitcoin Example
Bitcoin Transactions Are:
- Irreversible – After a bitcoin transaction has been confirmed, it can’t be reversed by anyone.
- Cheap – A bitcoin transaction can move thousands of dollars with a minimal transaction cost, which is on average a couple of dollars, depending on the size and desired speed of the transaction.

- Fast – The speed at which transactions can be processed depends on how much users are willing to pay. Bitcoin transactions can generally be confirmed within a few minutes.
- Global – Bitcoin can be sent to basically anyone, anywhere in the world.
- Anonymous – Bitcoin wallets don’t have names associated with them, so in theory, anyone can send bitcoin completely anonymously.

Prominent Cryptocurrencies
As of July 2022, the top ten cryptocurrencies are (ranked by market capitalization):
Each promises to solve a particular problem. Cardano, for instance, aims to solve prior cryptocurrency issues, like scalability (ensuring low transaction costs, even with a busy network), interoperability (able to connect with other blockchains) and sustainability (proof-of-work, for example, is very energy intensive and elevates carbon emissions).
Three of these currencies are actually pegged to the U.S. Dollar: Tether, USD Coin, and Binance USD. These make it easy to transact dollar amounts and buy crypto without needing traditional finance.
Where Can I Buy Cryptocurrency?
There are several ways that investors can buy crypto, but using crypto exchanges is one of the easiest and most popular methods.
Cryptocurrency exchanges are like forex brokers with a twist. Instead of trading a contract on the underlying instrument, you actually get to own the cryptocurrency. It’s like being delivered the gold you traded, just digitally.
Unlike a real gold delivery, exchanges often have minuscule fees, and coins are transferred instantly into your wallet.
Use a site like Binance, Coinbase, Bitstamp or Kraken. All of these exchanges have been around for many years and offer strong security features to help keep your coins safe.
Easy Access to Trading/Speculating With Cryptocurrencies
If you just want to trade crypto and don’t want to bother with the hassle of moving coins and potential security risks, your favorite forex broker likely offers contracts for difference (CFDs) that allow you to effortlessly trade cryptocurrencies.
This enables cryptocurrency traders to engage in both long (buy) and short (sell) crypto positions on the superb trading platforms offered by these brokers.
To make crypto trading even more exciting, many forex brokers offer leverage on cryptocurrency trades that can enhance your profits (and losses – always employ proper risk management!).
FAQs
What is the difference between Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies?
Bitcoin is the first and most well-known cryptocurrency, created in 2009 by an anonymous figure known as Satoshi Nakamoto. It introduced the concept of a decentralized digital currency, using blockchain technology to record transactions. Bitcoin’s primary purpose is to serve as “digital gold,” a store of value and medium of exchange. Other cryptocurrencies, often called “altcoins,” differ in their purposes and technologies.
For example, Ethereum, the second-largest cryptocurrency, enables smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps) on its blockchain, making it more versatile than Bitcoin. Altcoins like Litecoin and Ripple offer different features, such as faster transaction times or specific use cases in financial services.

How do I start investing in cryptocurrencies?
To start investing in cryptocurrencies, follow these steps:
- Set up a Crypto Wallet: Choose a digital wallet to store your cryptocurrencies. Options include software wallets (like Exodus) for convenience or hardware wallets (like Ledger) for enhanced security.
- Choose a Cryptocurrency Exchange: Sign up on a reputable exchange, such as Coinbase, Binance, or Kraken, where you can buy and sell cryptocurrencies.
- Purchase Cryptocurrency: Fund your exchange account using fiat currency (like USD) and buy the cryptocurrency of your choice. Ensure you transfer your assets to your crypto wallet for security.
Is cryptocurrency legal?
The legal status of cryptocurrencies varies by country. In the United States, cryptocurrencies are legal and regulated as property by the IRS, but specific regulations may vary by state. In the European Union, cryptocurrencies are also legal, with the EU working on comprehensive regulatory frameworks.
However, some countries like China have banned cryptocurrency trading and mining, while others, like El Salvador, have embraced Bitcoin as legal tender. It’s essential to check the local regulations in your country before investing.
What is digital money?
Digital money refers to cryptocurrencies, which are decentralized forms of currency that allow for transactions without the need for central banks or intermediaries. Digital money utilizes cryptographic technology to ensure secure transactions and maintains its legitimacy through blockchain, rather than traditional financial institutions.
*Check out our handy guide, How to Choose the Right Cryptocurrency Broker.