What is DeFi Yield Farming?
Last Update: November 28th, 2024

DeFi yield farming is an investment approach in decentralized finance (DeFi) where cryptocurrency holders earn passive income by lending or staking their assets on DeFi platforms. The term “yield” represents the returns or interest earned on these investments, while “farming” reflects the process of continuously generating income from digital assets.
Together, “yield farming” means maximizing returns on crypto holdings by participating in DeFi protocols designed to reward users who contribute liquidity.
Unlike traditional finance, where returns are often fixed and predictable, DeFi yield farming offers the potential for much higher, variable returns through decentralized platforms. Yield farmers earn interest, transaction fees, or newly issued tokens by contributing their assets to liquidity pools, which support decentralized exchanges and platforms by providing essential liquidity.
Key Points:
- Purpose: Yield farming enables users to earn rewards on crypto holdings by lending or staking assets.
- How It Works: Users contribute to liquidity pools on decentralized platforms, earning transaction fees, interest, or new tokens in return.
- Benefits:
- Higher Returns: Often provides higher yields than traditional financial products.
- Decentralized Structure: Operates without central intermediaries, offering greater access to financial tools and opportunities.
- Popularity: Yield farming has grown rapidly due to its potential for significant returns and its role in supporting the DeFi ecosystem.
- Risks: Includes exposure to market fluctuations, smart contract vulnerabilities, and impermanent loss, which can affect overall returns.
While yield farming can offer impressive returns, understanding the underlying risks and mechanisms is essential for participants looking to optimize their strategies in the DeFi ecosystem.
How Does Yield Farming Work?
Yield farming operates through a variety of DeFi methods that allow users to earn returns on their crypto assets by actively participating in decentralized finance ecosystems. Here’s a closer look at the primary mechanisms involved in yield farming:
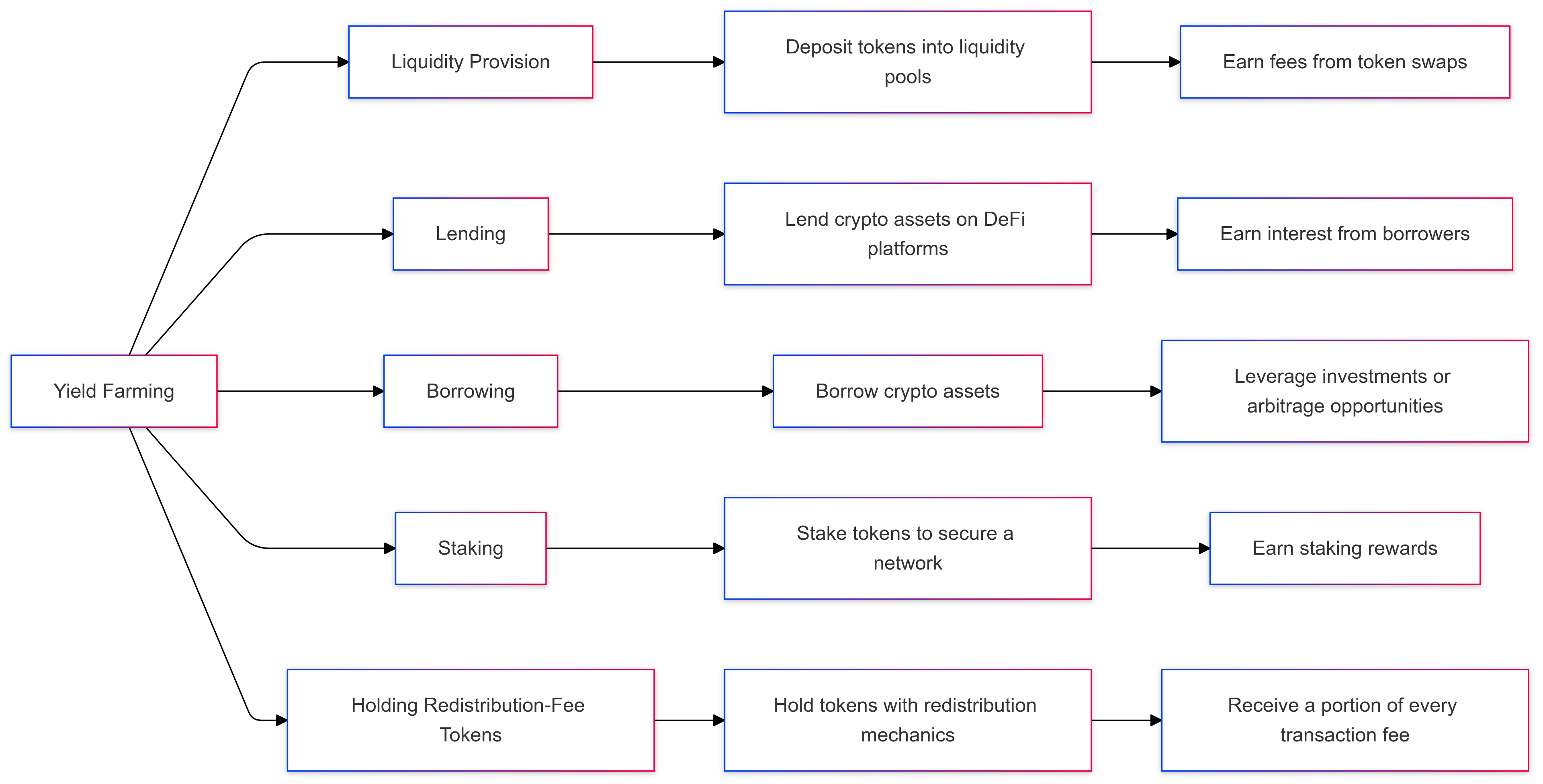
- Liquidity Provision
- In liquidity provision, users, or liquidity providers (LPs), deposit pairs of tokens (e.g., ETH/USDT) into a liquidity pool on decentralized exchanges (DEXs) like Uniswap or PancakeSwap.
- These liquidity pools facilitate trades on the exchange, and in return, LPs earn a share of the transaction fees generated within the pool.
- Example: An LP deposits equal amounts of ETH and USDT into a liquidity pool. Each time someone trades between ETH and USDT on the platform, a small fee is collected, with a portion distributed to the LPs as a reward.
- Lending
- Lending platforms such as Aave and Compound allow users to lend out their cryptocurrency in exchange for interest.
- These platforms facilitate loans by connecting borrowers with lenders, and lenders earn yield farming rewards in the form of interest on the lent amount, often higher than traditional banks.
- Example: A user deposits stablecoins (e.g., USDC) into Aave’s lending pool. Borrowers pay interest on the stablecoins they borrow, and a portion of this interest is passed back to the original lender.
- Borrowing
- In borrowing-based yield farming, users deposit collateral (often over-collateralized) to take out loans, typically in stablecoins.
- Borrowers can reinvest their loaned stablecoins into additional yield farming opportunities while retaining ownership of their collateral.
- Example: A user deposits Bitcoin as collateral, borrows USDT, and uses the USDT to participate in other DeFi yield farming activities.
- Staking
- Staking allows users to earn rewards by locking up tokens in a proof-of-stake (PoS) network, helping to secure the network and validate transactions.
- Many DeFi platforms, like PancakeSwap and Yearn Finance, offer staking rewards for native tokens, allowing users to earn additional income by contributing to the protocol’s stability.
- Example: A user stakes CAKE on PancakeSwap to earn additional CAKE tokens as a reward.
- Holding Redistribution-Fee Tokens
- Certain tokens redistribute transaction fees back to holders, allowing users to passively earn returns simply by holding the token.
- Example: Holding Safemoon earns users a portion of the transaction fees generated from Safemoon trades, automatically increasing the token balance over time.
How Yield Farmers Earn Rewards
Yield farmers earn rewards based on their level of participation in DeFi protocols. Rewards may include:
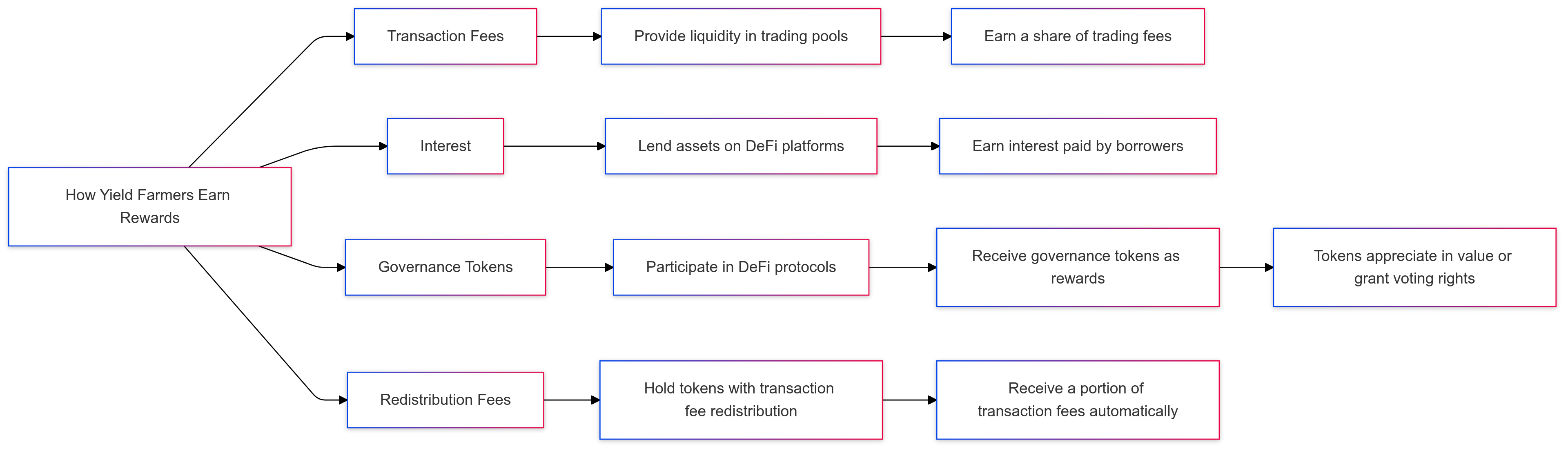
- Transaction Fees: Earned by providing liquidity in trading pools.
- Interest: Earned from lending or staking assets.
- Governance Tokens: Many DeFi platforms reward users with governance tokens, which can appreciate in value or provide voting rights within the protocol.
- Redistribution Fees: Collected by holders of specific tokens with built-in transaction fee redistribution.
By diversifying their activities across these methods, yield farmers maximize returns on their crypto assets while actively contributing to the functionality and liquidity of DeFi platforms. However, these methods also carry unique risks that yield farmers must consider before investing.
Key Concepts in Yield Farming
Yield farming involves several fundamental concepts that are essential to understanding how it works and the risks involved. Here’s a breakdown of the key concepts:
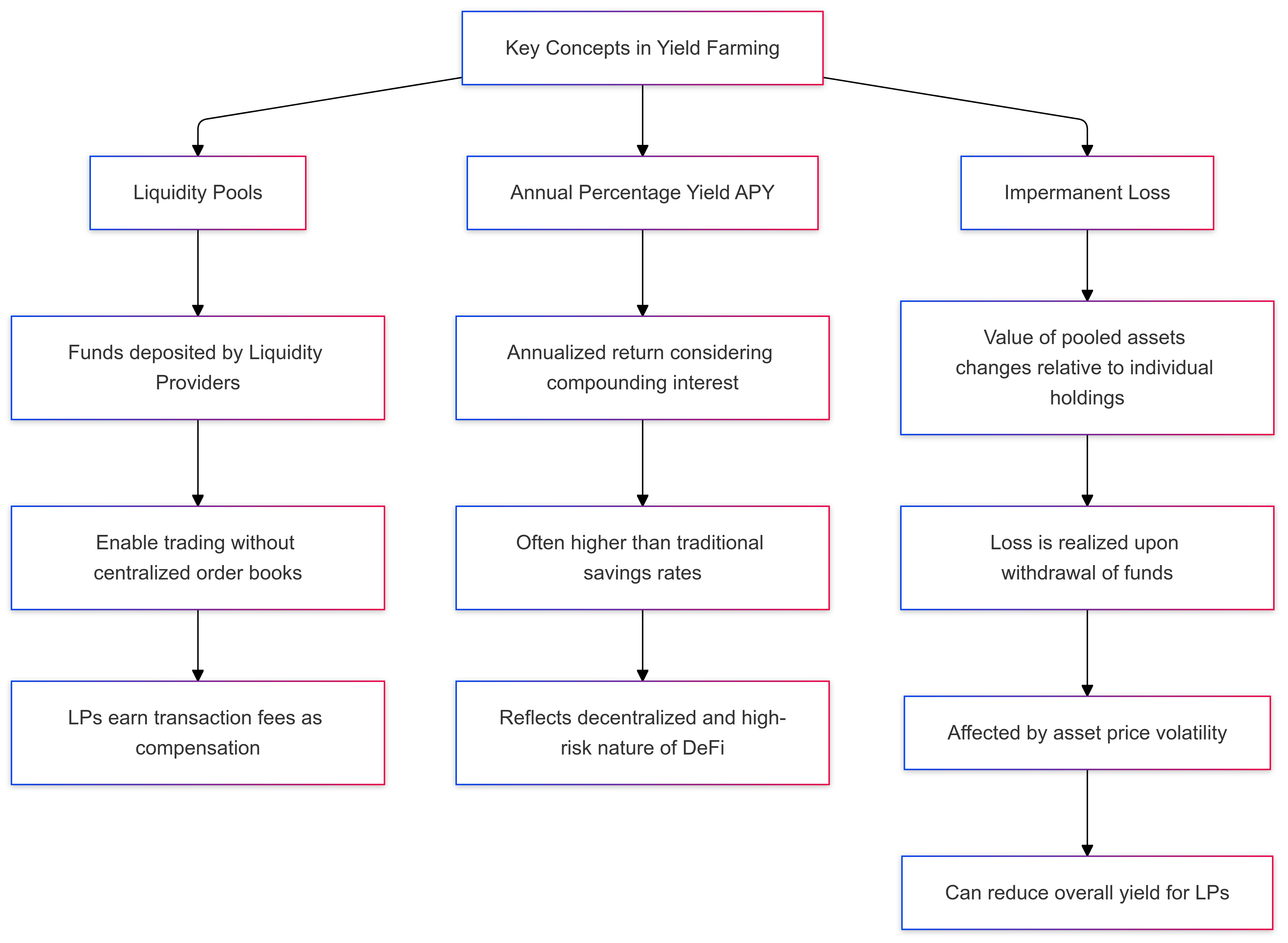
- Liquidity Pools
- Liquidity pools are collections of funds deposited by users, known as liquidity providers (LPs), into a decentralized exchange (DEX). These pools enable trading between different cryptocurrencies without the need for a centralized order book.
- Example: On Uniswap, an LP can deposit an equal amount of ETH and USDC into a pool. Traders then use this pool to swap between ETH and USDC, with LPs earning a portion of the transaction fees as compensation.
- Annual Percentage Yield (APY)
- APY represents the annualized rate of return on an investment, taking compounding interest into account. In DeFi yield farming, APY can vary greatly and is often much higher than traditional savings accounts, reflecting the decentralized and high-risk nature of the ecosystem.
- Example: A yield farming platform might offer an APY of 15% for lending USDT, meaning the user would earn 15% on their USDT holdings over a year, assuming stable rates.
- Impermanent Loss
- Impermanent loss occurs when the value of assets in a liquidity pool changes relative to the value of holding those assets individually. This loss happens due to the volatility of the assets in the pool and is only “impermanent” until the assets are withdrawn, at which point it may become realized.
- Example: An LP deposits ETH and USDC into a liquidity pool. If the price of ETH rises significantly while the funds are in the pool, the LP may lose out on some gains compared to holding ETH directly. The LP experiences an impermanent loss if they withdraw the assets at this point, potentially affecting overall yield.
These concepts—liquidity pools, APY, and impermanent loss—are crucial for yield farmers to understand, as they determine potential returns and risks within yield farming strategies. Awareness of these elements helps yield farmers make informed decisions and manage expectations in the high-risk, high-reward landscape of DeFi yield farming.
Popular Yield Farming Platforms
Yield farming has grown rapidly across various DeFi platforms, each offering unique features and rewards for users who provide liquidity. Here are five of the most popular platforms for yield farming:
1. Uniswap
- Overview: Uniswap is a leading decentralized exchange (DEX) on the Ethereum blockchain, known for its role in pioneering automated liquidity provision.
- Unique Features: Uniswap allows users to create liquidity pools for any token pair on Ethereum, enabling peer-to-peer trading through an automated market maker (AMM) system.
- Governance Token: Uniswap’s governance token, UNI, gives holders voting rights on protocol changes, which allows the community to shape the platform’s future.
- Advantages: Uniswap’s popularity means high liquidity, and the simplicity of the platform makes it accessible to beginners. By providing liquidity, users can earn transaction fees from each trade within their liquidity pools, contributing to potentially high yields.
2. Aave
- Overview: Aave is an open-source lending and borrowing protocol that allows users to earn interest on their crypto assets or take out collateralized loans.
- Unique Features: Aave is known for its Flash Loans—instant, uncollateralized loans that must be repaid within the same transaction, offering unique arbitrage and profit opportunities.
- Governance Token: Aave’s governance token, AAVE, enables users to vote on protocol updates and earn rewards.
- Advantages: Aave’s wide range of supported assets and competitive interest rates make it an attractive platform for yield farming. With Flash Loans, users can engage in unique strategies that wouldn’t be possible with traditional loans, such as arbitrage between pools or interest rate optimization.

3. PancakeSwap
- Overview: PancakeSwap is a DEX on the Binance Smart Chain (BSC), known for its lower transaction fees and faster processing times compared to Ethereum-based platforms.
- Unique Features: PancakeSwap offers features like staking, farming, and NFT trading. The platform’s lottery and prediction games also provide unique engagement opportunities for users.
- Governance Token: CAKE is PancakeSwap’s native token, allowing users to participate in governance and stake their CAKE to earn more CAKE or other tokens.
- Advantages: PancakeSwap’s low fees on BSC make it an affordable choice for smaller investors. The range of staking pools and yield farming opportunities allows users to diversify their strategies, making it popular for both new and experienced farmers.
4. Curve Finance
- Overview: Curve Finance is a decentralized exchange optimized for stablecoin trading and low-slippage trades, which helps minimize impermanent loss for liquidity providers.
- Unique Features: Curve’s algorithm is designed specifically for stablecoin swaps, making it ideal for users looking to farm yields with minimized volatility risk.
- Governance Token: The platform’s token, CRV, is used for governance, allowing holders to vote on upgrades and earn rewards based on their participation in the ecosystem.
- Advantages: Curve Finance is a go-to platform for yield farmers seeking stable returns with minimal exposure to impermanent loss. By focusing on stablecoins, Curve provides lower risk while still offering higher returns than traditional finance, appealing to conservative investors.
5. Yearn Finance
- Overview: Yearn Finance is an Ethereum-based platform that aggregates yield farming opportunities across multiple DeFi platforms, allowing users to optimize returns.
- Unique Features: Yearn’s Vaults function as pooled yield farming strategies, where users deposit funds and Yearn’s algorithms automatically allocate assets to the highest-yielding opportunities.
- Governance Token: YFI is Yearn’s governance token, known for its scarcity, and allows holders to propose and vote on platform upgrades.
- Advantages: Yearn’s Vaults are user-friendly and ideal for hands-off investors, as they automate the process of finding optimal returns across platforms. With a strong reputation and a highly active community, Yearn Finance provides a reliable solution for investors looking to simplify their yield farming strategy.
These five platforms—Uniswap, Aave, PancakeSwap, Curve Finance, and Yearn Finance—are key players in the DeFi space, each offering unique advantages for yield farming.
Pros and Cons of Yield Farming
Yield farming offers the potential for high returns and passive income, but it also comes with its own set of risks. Here’s a look at some of the key advantages and disadvantages of yield farming:
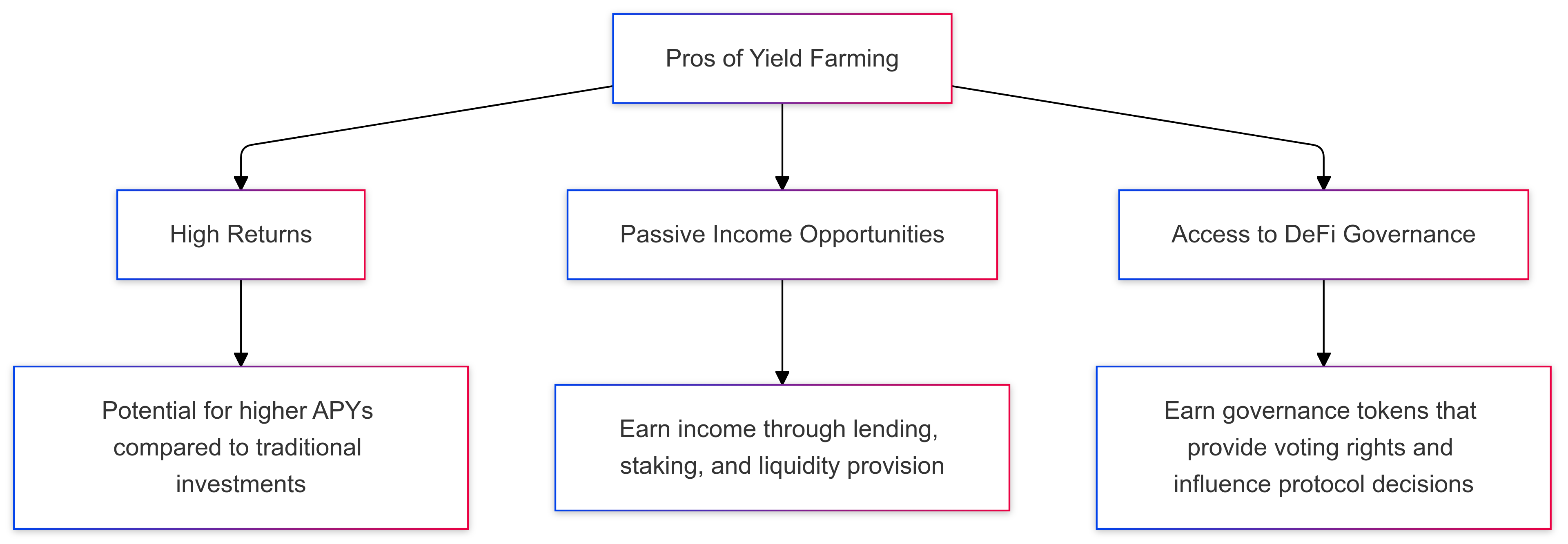
Pros of Yield Farming
- High Returns
- Yield farming often provides significantly higher returns than traditional financial products, attracting investors seeking substantial profits. With the potential for annual percentage yields (APYs) far above bank interest rates, yield farming has become a popular way to grow crypto assets.
- Passive Income Opportunities
- By contributing to liquidity pools or staking, yield farmers can earn income passively without actively managing their investments. This allows users to generate consistent rewards, which can be particularly appealing for long-term holders looking to maximize their assets.
- Access to DeFi Governance
- Many yield farming platforms offer governance tokens as rewards, giving holders voting rights in protocol decisions. This decentralized governance model allows users to have a voice in the platform’s future and direction, often providing additional value as the token appreciates.
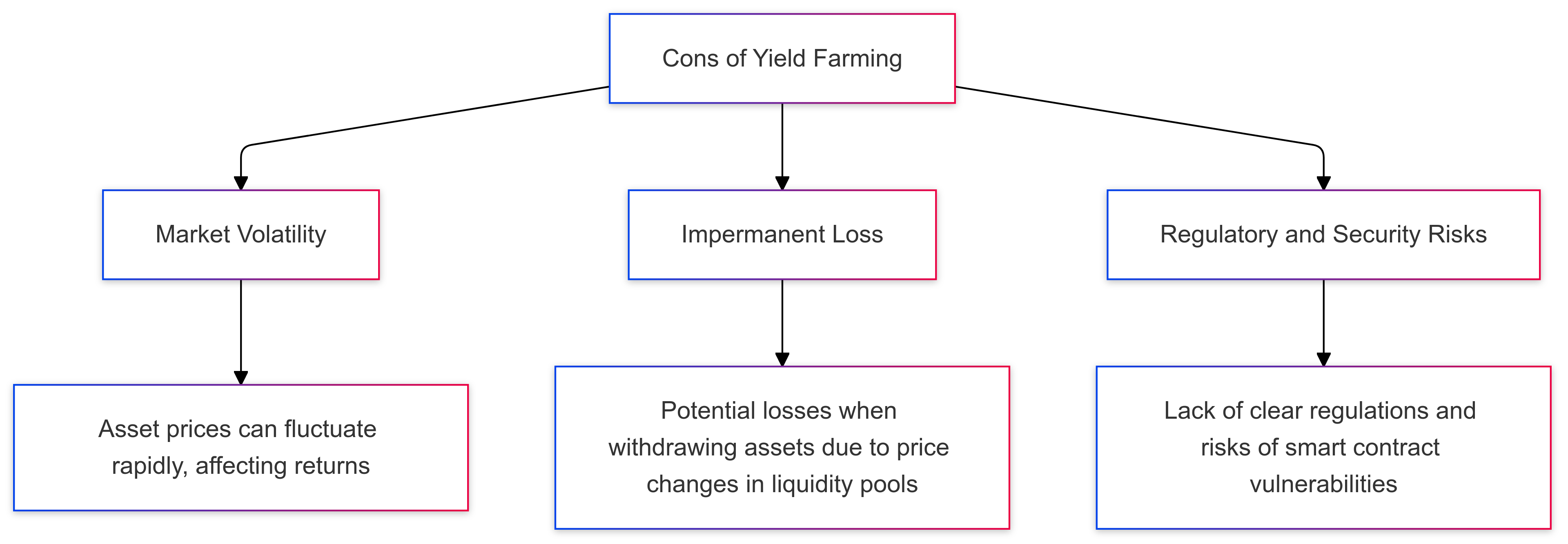
Cons of Yield Farming
- Market Volatility
- Cryptocurrency markets are highly volatile, and this instability can lead to large, unpredictable swings in returns. Yield farming returns fluctuate with token prices, and in bear markets, the value of rewards can decline substantially, affecting overall profitability.
- Impermanent Loss
- When providing liquidity in pairs, impermanent loss occurs if one asset’s price changes significantly relative to the other. This loss can reduce or even negate the profits from yield farming, especially when one token in a pool experiences high volatility. For many, impermanent loss is one of the biggest risks in yield farming.
- Regulatory and Security Risks
- Yield farming operates in the largely unregulated DeFi ecosystem, which poses risks around regulatory uncertainty and smart contract vulnerabilities. Regulatory changes could impact the viability of certain platforms, and if smart contracts are compromised, investors could lose their funds due to security breaches.
Yield farming offers attractive income opportunities and the chance to participate actively in the DeFi ecosystem.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Yield Farming
Yield farming can be highly rewarding, but it also comes with risks that can lead to substantial losses if not managed carefully. Here are some common mistakes yield farmers should avoid and practical tips to navigate these pitfalls:
- Ignoring Market Conditions
- Market conditions play a major role in yield farming returns. Entering or exiting yield farming positions without considering broader market trends can lead to poor timing and increased risk, especially during periods of high volatility.
- Tip: Regularly monitor market trends and economic news that may impact cryptocurrency prices. Adjust strategies accordingly to minimize exposure to market downturns.
- Over-Leveraging
- Over-leveraging is a common trap in yield farming, especially for those looking to maximize short-term gains. Borrowing too much can amplify losses if the market moves against the position, quickly eroding capital.
- Tip: Use leverage sparingly and maintain a conservative approach. Only borrow amounts that can be managed safely, and set stop-losses to limit potential losses.
- Inconsistent Strategies
- Frequently changing strategies or yield farming across too many protocols can dilute returns and increase transaction costs. Inconsistent approaches can make it difficult to track performance and manage risks effectively.
- Tip: Develop a clear strategy and stick to it, regularly reviewing its performance. Choose a few reliable protocols and avoid switching frequently to reduce fees and improve tracking.
- Underestimating Impermanent Loss
- Many yield farmers underestimate the impact of impermanent loss, which can reduce profits in volatile markets. Ignoring this risk, especially in highly volatile token pairs, can lead to unexpected losses.
- Tip: Research impermanent loss and consider its impact on returns, particularly in liquidity pools with volatile assets. Stablecoin pairs can be a safer option for reducing this risk.
By recognizing and avoiding these common mistakes, yield farmers can better manage risk and create a more stable path toward achieving their financial goals in the DeFi ecosystem.
Getting Started with Yield Farming in DeFi
Yield farming can be a profitable way to grow crypto assets, but for beginners, it’s essential to start with a well-structured approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide to getting started with yield farming in decentralized finance (DeFi):
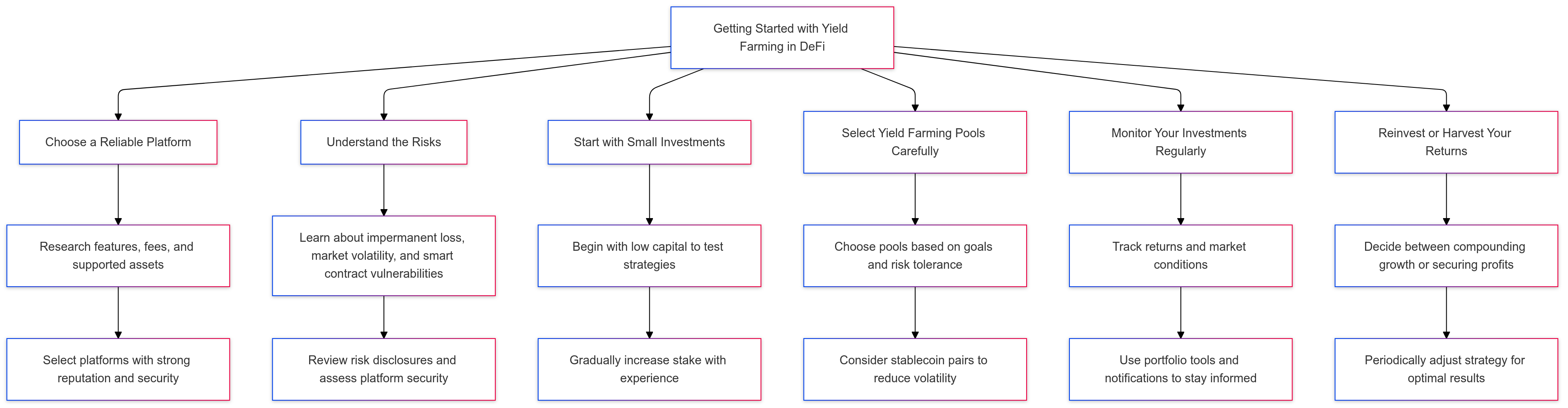
- Choose a Reliable Platform
- Selecting the right platform is the first step. Popular platforms like Uniswap, Aave, PancakeSwap, and Yearn Finance offer diverse yield farming options with varying levels of risk. Each platform has its own set of features, fees, and supported assets, so researching options is crucial.
- Tip: Look for platforms with a strong reputation, transparent fees, and user-friendly interfaces. Reading community reviews or exploring each platform’s documentation can provide additional insights into their features and security.
- Understand the Risks
- Yield farming comes with significant risks, including impermanent loss, market volatility, and smart contract vulnerabilities. Before investing, it’s essential to understand these risks and be prepared for possible losses.
- Tip: Review each platform’s risk disclosures and research impermanent loss to understand how it might impact your returns. Familiarize yourself with each platform’s smart contract, if possible, to assess security risks.
- Start with Small Investments
- Starting small allows beginners to familiarize themselves with yield farming mechanics without risking large amounts of capital. Use initial investments to test different strategies and learn how the platform operates.
- Tip: Avoid investing more than you can afford to lose in your first yield farming venture. Gradually increase your stake as you gain confidence and experience.
- Select Yield Farming Pools Carefully
- Yield farming often requires contributing to liquidity pools in pairs, such as ETH/USDT or BTC/DAI. Choose pools that align with your investment goals and risk tolerance, as some pairs are more volatile than others.
- Tip: Stablecoin pairs, like USDC/USDT, are typically less volatile and may be a good starting point for beginners who want to minimize impermanent loss.
- Monitor Your Investments Regularly
- The DeFi market is dynamic, and returns can fluctuate with market conditions. Regularly monitoring your investments allows you to make adjustments as needed, ensuring you optimize your returns.
- Tip: Set up notifications or use portfolio tracking tools to stay informed about yield changes, impermanent loss, or significant shifts in the pool’s asset value. This can help you make timely decisions to protect or enhance your investment.
- Reinvest or Harvest Your Returns
- Decide on a strategy for reinvesting or harvesting your rewards. Reinvesting can lead to compound growth, while harvesting allows you to secure your earnings.
- Tip: Consider periodically harvesting your returns to lock in profits, or reinvest in the same or different pools if your goal is long-term growth.
By following these steps, beginners can enter the world of yield farming with a balanced approach, managing risks while exploring the benefits of DeFi. Starting small, staying informed, and refining strategies over time will build confidence and increase the likelihood of success in yield farming.

Conclusion
Yield farming in DeFi offers the opportunity to earn substantial returns by leveraging crypto assets in various protocols. By providing liquidity, lending, staking, and participating in liquidity pools, yield farmers can benefit from passive income and exposure to innovative decentralized finance platforms.
However, the potential for high rewards comes with notable risks, including market volatility, impermanent loss, and security vulnerabilities associated with smart contracts. For beginners, understanding these risks and starting with small, manageable investments is essential. Choosing reliable platforms, monitoring investments, and having a clear strategy can help manage risk and enhance returns over time.
While yield farming can be a lucrative addition to a crypto portfolio, it requires a solid foundation of knowledge and ongoing attention to market conditions. By approaching yield farming with caution and a willingness to learn, readers can make informed decisions and explore the potential of DeFi in a way that aligns with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
FAQ
1. What is DeFi Yield Farming?
- Answer: DeFi yield farming is an investment approach in decentralized finance where cryptocurrency holders earn passive income by lending or staking their assets on DeFi platforms. By contributing liquidity, yield farmers can earn rewards in the form of interest, transaction fees, or new tokens, which can often yield higher returns than traditional financial products.
2. How Does Yield Farming Work?
- Answer: Yield farming involves several methods, including liquidity provision, lending, borrowing, and staking. Users deposit tokens into liquidity pools or lend them on platforms, earning rewards for their contributions. For instance, a user might lend USDT on Aave and earn interest or provide ETH/USDT to a Uniswap pool, collecting a share of transaction fees.
3. What Are the Key Risks in Yield Farming?
- Answer: Yield farming carries various risks, such as market volatility, impermanent loss (where pooled assets may lose value), and smart contract vulnerabilities. Because DeFi is largely unregulated, yield farmers are exposed to potential security breaches, market crashes, or regulatory changes that could impact returns.
4. What Are the Pros and Cons of Yield Farming?
- Answer: Pros of yield farming include high potential returns, passive income generation, and participation in DeFi governance. However, the cons involve market volatility, impermanent loss, and regulatory uncertainties. Yield farmers must understand these risks to make informed decisions about where and how to invest.
5. How Can Beginners Start Yield Farming Safely?
- Answer: Beginners should start yield farming by choosing a reputable platform, understanding risks, and starting with a small investment. It’s also crucial to monitor investments regularly and consider low-volatility pairs, such as stablecoins, to reduce risk. Building a consistent strategy and learning about the market will help in navigating the high-reward, high-risk DeFi space effectively.
Sidebar rates
HFM
wgt-lc-defi
- DeFi Lending
- DeFi Yield Farming
- AMM (Automated Market Maker)
- DEX
- Cross Chain Bridges
- Crypto Options
- Tokenized Bonds
- Crypto Derivatives
- On-chain synthetic Assets
- Cryptocurrency Perpetuals
- Cryptocurrency Staking
- Cryptocurrency Total Locked Value (TVL)
- Impermanent loss
- Rebase Token
- Decentralized Autonomous Organization
- Decentralized Application
- Gas Fees
- Liquidity Pools
- Cryptocurrency Tokenomics
- Pegged Stablecoins
