Bitcoin cash is a cryptocurrency that was founded in August 2017, a peer-to-peer electronic cash system that proposes to become sound global money with fast payments, privacy, micro fees and high transaction capacity (big blocks). Bitcoin Cash payments are transferred directly from one person to another, the same way that physical money, such as a dollar bill, is handed directly to the person being paid.
It is also worth mentioning that, as a permissionless, decentralized cryptocurrency, Bitcoin Cash does not need any central bank or trusted third parties. Furthermore, Bitcoin Cash does not depend on monetary middlemen such as banks and payment processors, unlike traditional fiat currency. The transactions tend not to be controlled by governments or other centralized corporations. Likewise, funds cannot be frozen or caught, as financial third -parties have no authority to control the Bitcoin Cash network.
From a historical viewpoint, the average size of a block on Bitcoin’s blockchain was just under 100 KB during 2010. The average fee for a transaction amounted to a couple of cents. This made the Bitcoin blockchain vulnerable to attacks, entirely made up of cheap transactions, that could have crippled the system. Thus, the size of a block on Bitcoin’s blockchain was limited to 1 MB, to prevent such a situation. Each block was generated every 10 minutes, allowing for space and time between consecutive transactions. Limiting the size and time required to generate a block added another layer of security to Bitcoin’s blockchain.
Uses of Bitcoin Cash:
It is worth recalling that Bitcoin Cash combines scarcity of a gold-like nature with the spendability of cash. Due to the limited total supply of 21 million coins, Bitcoin Cash is rare and it can easily be used like physical cash. As we have already mentioned, Bitcoin cash transactions are fast, and transaction fees are normally less than one-tenth of a cent. The majority of people can accept Bitcoin Cash payments with a computer or smartphone.
As a result, Bitcoin Cash can be used in many situations. Besides the peer-to-peer payments between individuals, Bitcoin Cash can also be used to pay participating retailers for goods and services in-store and online. Moreover, Bitcoin Cash also diminishes the charges and settlement times for payments and cross-border trade. In addition to this, the use of Bitcoin Cash includes tokens, simplified smart contracts, and private payments with tools such as CashShuffle and CashFusion.
The difference between Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash:
During 2017, the Bitcoin project and its team were divided regarding two different concerns about the scalability of the cryptocurrency. As a result, Bitcoin Cash created a new cryptocurrency, which all supporters considered to be the legitimate continuation of the Bitcoin project, in the form of peer-to-peer electronic cash. As a result of this division (block 478,558), the holders of Bitcoins automatically became owners of Bitcoin Cash.
In contrast to Bitcoin BTC, Bitcoin Cash proposes to scale itself in order to meet the global payment system demands. During the division, the Bitcoin Cash block size rose from 1MB to 8MB, which means that Bitcoin Cash can now handle significantly more transactions per second (TPS), whilst keeping fees very cheap.
Major Factors that Influence the Bitcoin (BTC):
- The supply of bitcoin and the demand for it on the market
- The cost of generating a bitcoin via the mining method
- The awards issued to bitcoin miners for verifying transactions to the blockchain
- The number of competing cryptocurrencies
- The exchanges it trades on
- Regulations governing its sale
- Its internal governance
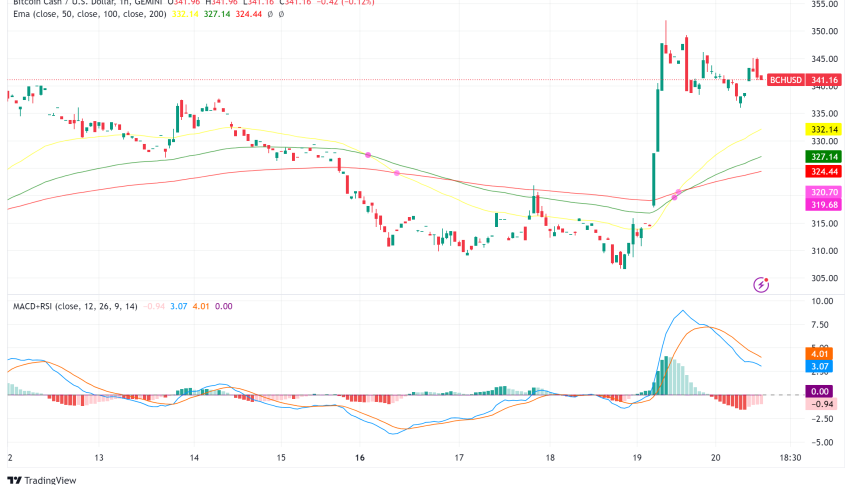
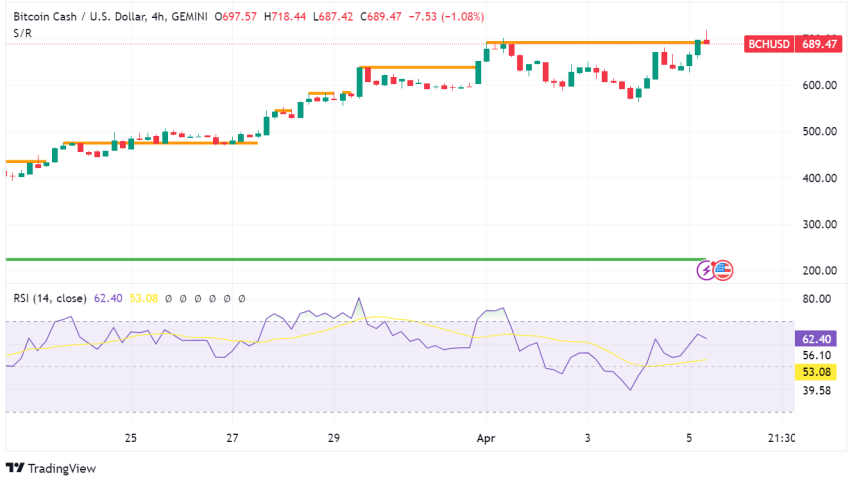
Bitcoin Cash (BCH) – Historical Price Charts and Data
Now, let me explain some significant factors that impact Bitcoin (BTC) significantly:
Cost of Production:
Electricity consumption could be considered as one of the most critical factors in the mining process, by far. Bitcoin ‘mining’ depends on complicated cryptographic math problems that all miners have to solve. The first one to do so is rewarded with a block of newly minted bitcoins, and any transaction fees that have accumulated since the last block was found. Unlike other produced goods, Bitcoin’s algorithm only allows for one block of Bitcoins to be found, on average, once every ten minutes. That means that the higher the number of generators who join in the race for solving the math problem, the more difficult – and thus the more expensive – it becomes to solve the problem and preserve that ten-minute interval.
Supply and Demand:
The supply of Bitcoin is normally effected in two different ways. Firstly, the Bitcoin protocol allows new Bitcoins to be created at a fixed rate. New Bitcoins are introduced into the market when miners process blocks of transactions, and the rate at which new coins are introduced is designed to slow down over time. Case in point: growth slowed from 6.9% (2016), to 4.4% (2017) to 4.0% (2018). In turn, the demand for Bitcoins tends to increase faster than the supply increases, which can underpin the price. The slowing of Bitcoin circulation growth is due to the halving of block rewards offered to Bitcoin miners and can be thought of as artificial inflation for the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
On the other hand, the supply could also be impacted by the number of Bitcoins the system allows to exist. This number is capped at 21 million, whereby once this number has been reached, mining activities will no longer create new Bitcoins. For example, the supply of Bitcoins was 18.1 million in December 2019, representing 86.2% of the supply of Bitcoins that will ultimately be made available. As soon as 21 million Bitcoins are in circulation, prices will depend on whether it is considered practical (readily usable in transactions), legal and in demand, which will be determined by the popularity of other cryptocurrencies. The artificial inflation mechanism of the halving of block rewards will no longer impact the price of the cryptocurrency. However, at the current rate of adjustment of block rewards, the last Bitcoin is not set to be mined until 2140.