Cobalt is a chemical element with the symbol Co and the atomic number 27. It is normally only found in the earth’s crust in a chemically combined form. It is a free element that is produced by reductive smelting. Cobalt is a by-product of nickel and copper; therefore, most cobalt is produced during nickel and copper production. Pure metallic cobalt is a hard, shiny, silver-gray metal, that is traditionally used in various industrial applications, such as high-temperature superalloys (mainly in jet turbines), hard facing products, stainless steels, cemented carbides and medical prosthetics. In the past few years, lithium-ion batteries have become an increasingly important end-use for cobalt, due to the advances in the electric vehicle (EV) industry.
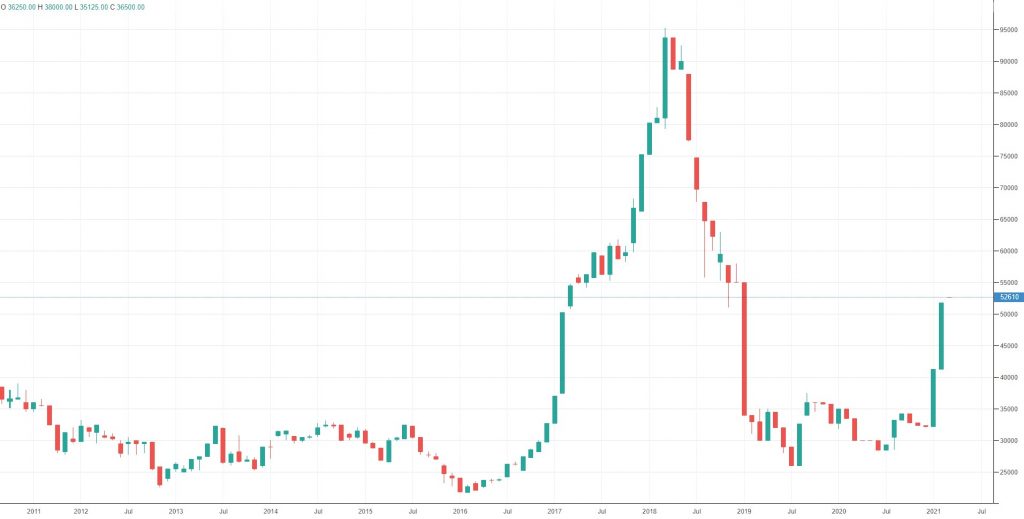
10 Years Historical Price of Cobalt- Monthly Chart
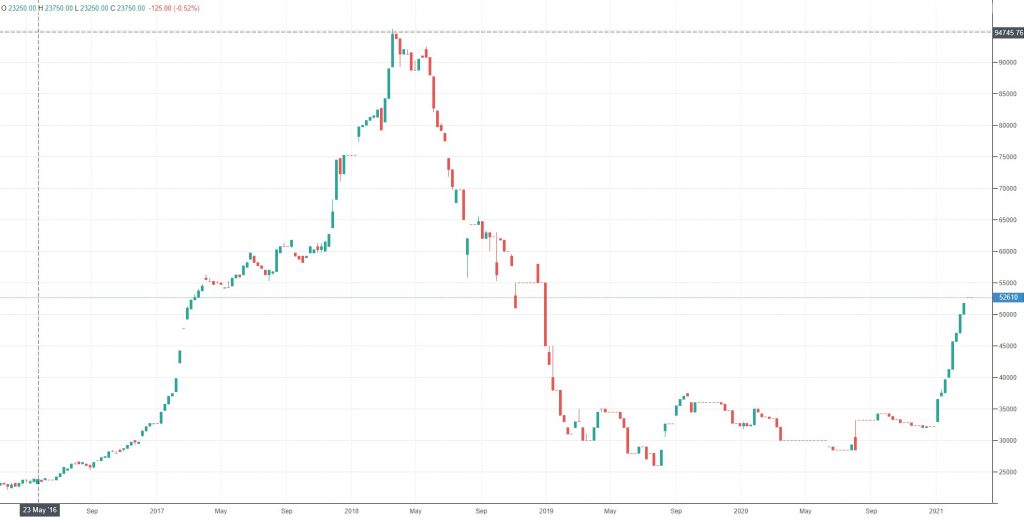
10 Years Historical Price of Cobalt- Weekly Chart
Cobalt Market Overview:
The growth of the worldwide cobalt market is largely dependent on the demand for rechargeable batteries. These batteries are broadly used in a wide range of applications, including electric vehicles and small portable electronic devices, like notebook computers, mobile phones, games and power tools. Cobalt plays a key role in the chemistry of lithium-ion batteries. We all know that Li-ion batteries have more energy, power density and cycling ability than other batteries. These features are useful in hybrid cars, electric vehicles and the storage systems used on renewable energy farms. The ever-increasing usage of Li-ion batteries in electric vehicles is seen as the leading factor that will boost the demand for cobalt in the coming years. Several industry experts believed that the growth of the global electric-vehicle (EV) industry would result in a 4-fold rise in the demand for cobalt by 2020 (from 2018 levels), and they predict that it will increase 11-fold by 2027.
Another driving factor for the market growth could be the increased use of cobalt for metallurgical uses, primarily in high-temperature alloys (superalloys). Superalloys are extensively used in the gas turbine industry, in which elevated resistance to temperature and thermal oxidation are important material considerations. Cobalt-based superalloys are largely used to make jet turbines and industrial gas turbines. The rapid growth of the aerospace industry underpins the demand for aerospace engines and here, in turn, cobalt-based superalloys are expected to increase in the coming years.
Apart from this, cobalt-based alloys are also used to produce cemented carbides to make the hard alloys used in drilling tools. Cobalt can also deliver wear resistance when used in casting and forging processes. The increased use of drilling tools in the transportation and construction industry has favored market growth during the review period.
Uses of Cobalt:
- Cobalt is used in alloys for aircraft engine parts and alloys with corrosion/wear-resistant uses.
- Cobalt is broadly used in batteries and electroplating.
- Cobalt salts are also used to create blue and green colors in glass and ceramics.
- Radioactive 60Co is used in the treatment of cancer.
- Cobalt is necessary for many living creatures and it is a component of Vitamin B12.
- Cobalt is also used in the permanent samarium-cobalt magnets in high-speed motors and guitar pickups.
Price prediction:
It is estimated that the demand for cobalt could rise from 2k tonnes to over 300k tonnes in 2030. That is a 14,900% increase in demand. However, the cobalt chart is the only one you need to understand. Thanks to the electric vehicle revolution and a massive supply chain bottleneck coming out of Africa, cobalt will never be cheap again.
What Drives the Price Of Cobalt?
The two leading trade factors that drive the price of cobalt:
- Demand Surge:
Every single vehicle manufacturer will have to build their cobalt pipeline, and as we have already mentioned, at some $ 60,000 per metric ton, cobalt is the most expensive of the battery metals. The auto industry is certainly all about EVs now, and everyone is playing a furious game of catch-up with Tesla.
- Chinese Market:
The big automobile manufacturers are playing catch-up with Tesla, but China is set to challenge global cobalt supplies seriously. We were aware of this before, but now it’s becoming even clearer, as China is one of the world’s largest consumers of cobalt. China is expected to see a 12% increase in cobalt consumption on the back of EV and battery growth.
The world’s biggest cobalt producing countries
- Congo – 90,000t.
- Russia – 5,900t.
- Cuba – 4,900t.
- Australia – 4,700t.
- The Philippines – 4,600t.
- Canada – 3,800t.
- Madagascar – 3,500t.
- Papua New Guinea – 3,200t.
